Expecting a baby is a life-changing event that brings immense joy and responsibility. Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial during pregnancy to support the mother’s health and the baby’s development. Prenatal vitamins play a vital role in filling nutritional gaps and ensuring the well-being of both. These supplements provide essential nutrients, such as folic acid, iron, and calcium, that are necessary for a healthy pregnancy. By understanding the importance of prenatal vitamins, expectant mothers can take a proactive approach to their health and their baby’s health, setting the stage for a positive pregnancy experience and a healthy birth outcome.

The Importance of Prenatal Vitamins for a Healthy Pregnancy
Prenatal vitamins play a crucial role in ensuring the health and wellness of both the mother and the developing fetus during pregnancy. These supplements are specifically designed to provide essential nutrients that are vital for a healthy pregnancy. The nutrients found in prenatal vitamins support the mother’s health and the baby’s development, helping to prevent complications and birth defects.
Nutrients Found in Prenatal Vitamins
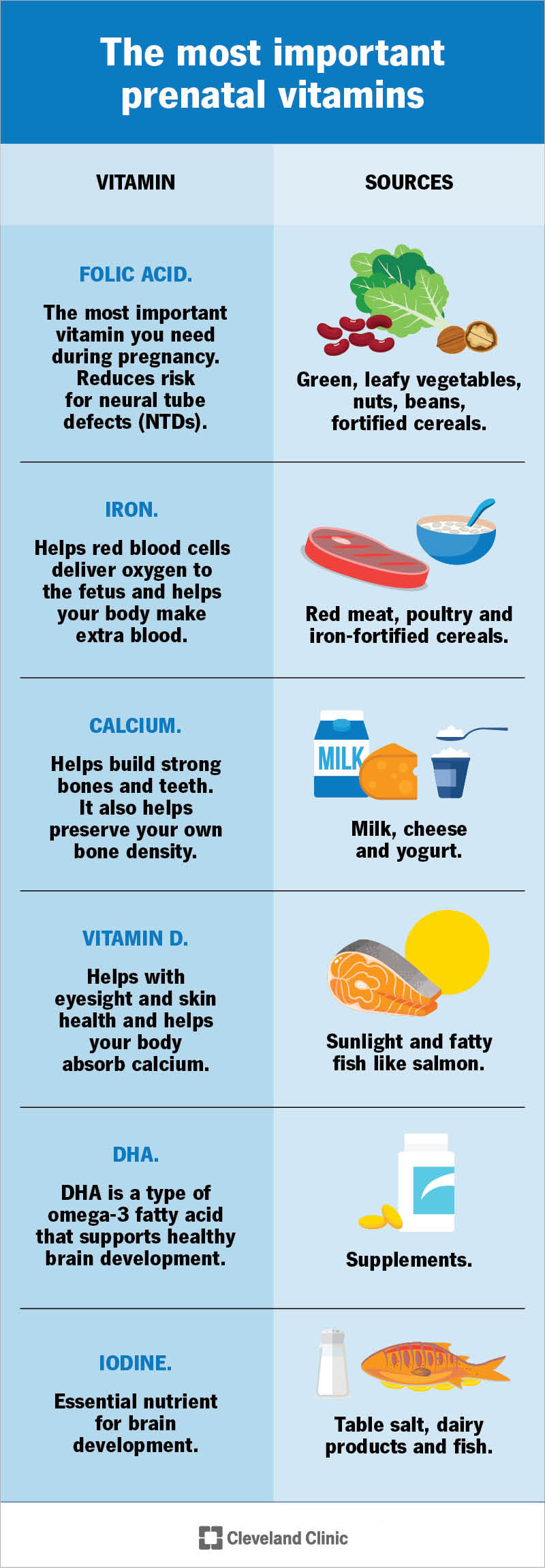
Prenatal vitamins contain a blend of vitamins and minerals that are crucial for pregnancy wellness. Some of the key nutrients include folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Folic acid is particularly important as it helps prevent neural tube defects in the baby. Iron supports the mother’s health by preventing anemia, while calcium is essential for the development of the baby’s bones, teeth, and muscles. Omega-3 fatty acids support the baby’s brain and eye development.
| Nutrient | Importance |
|---|---|
| Folic Acid | Prevents neural tube defects |
| Iron | Prevents maternal anemia |
| Calcium | Supports fetal bone development |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Supports fetal brain and eye development |
Benefits of Taking Prenatal Vitamins
The benefits of taking prenatal vitamins are numerous. They help fill any nutritional gaps in the mother’s diet, ensuring that both she and the baby receive the necessary nutrients for optimal health. Prenatal vitamins can help prevent birth defects, support the mother’s overall health, and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
When to Start Taking Prenatal Vitamins
It is recommended to start taking prenatal vitamins at least one month before conception to ensure that the body has adequate stores of essential nutrients. Continuing to take prenatal vitamins throughout pregnancy and during breastfeeding can provide ongoing benefits for both mother and baby.
Choosing the Right Prenatal Vitamin
Not all prenatal vitamins are created equal. When choosing a prenatal vitamin, look for a product that contains the essential nutrients mentioned earlier, such as folic acid and iron. Also, consider the form of the vitamin; some women may prefer gummies or capsules over traditional tablets.
Potential Side Effects of Prenatal Vitamins
While generally safe, prenatal vitamins can cause some side effects, such as nausea or constipation. These side effects can often be minimized by taking the vitamin with food or switching to a different brand or form of the vitamin.
| Side Effect | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Take with food or try a different brand |
| Constipation | Increase fluid intake and consider a dietary fiber supplement |
What is the best prenatal vitamin to take while pregnant?

The best prenatal vitamin to take while pregnant is a crucial decision for expectant mothers to ensure they are getting the necessary nutrients for a healthy pregnancy. Prenatal vitamins typically contain a combination of essential vitamins and minerals, including folic acid, iron, and calcium. These nutrients play a vital role in supporting the health and development of the fetus, as well as the mother’s overall well-being.
Key Ingredients to Look for in a Prenatal Vitamin
When selecting a prenatal vitamin, it’s essential to look for certain key ingredients that support fetal development and maternal health. A good prenatal vitamin should contain folic acid, which prevents birth defects of the brain and spine, iron, which supports the production of red blood cells, and calcium, which is crucial for fetal bone development.
- Folic acid (400-800 mcg) to prevent birth defects
- Iron (27 mg) to support red blood cell production
- Calcium (200-300 mg) for fetal bone development
Types of Prenatal Vitamins Available
Prenatal vitamins come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and gummies. Some prenatal vitamins are also specifically formulated to address certain dietary needs or restrictions, such as vegan or gluten-free options.
- Tablets or capsules for those who prefer traditional supplements
- Gummies for those who have difficulty swallowing pills
- Vegan or gluten-free options for those with dietary restrictions
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Prenatal Vitamin
When choosing a prenatal vitamin, expectant mothers should consider several factors, including the vitamin’s nutritional content, price, and brand reputation. It’s also essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best prenatal vitamin for individual needs.
- Nutritional content and ingredient list
- Price and insurance coverage
- Brand reputation and third-party testing
What is the best prenatal vitamin to get pregnant?

The best prenatal vitamin to get pregnant is a crucial aspect of preconception care. When trying to conceive, it’s essential to ensure that the body is receiving the necessary nutrients to support a healthy pregnancy. A well-chosen prenatal vitamin can help fill any nutritional gaps in the diet, increasing the chances of a successful conception and a healthy pregnancy.
Key Nutrients for Conception
A prenatal vitamin that contains the right blend of nutrients is vital for conception. Folic acid, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids are some of the essential nutrients that play a critical role in fetal development and preparation for pregnancy. A good prenatal vitamin should contain:
- Folic acid to prevent birth defects of the brain and spine
- Iron to support the production of red blood cells and prevent anemia
- Omega-3 fatty acids to support fetal brain development
Preconception Nutrition Considerations
When selecting a prenatal vitamin, it’s crucial to consider the nutritional needs of the body before conception. A good prenatal vitamin should be rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support overall health and well-being. Some key considerations include:
- A prenatal vitamin that contains antioxidants like vitamin C and vitamin E to protect against oxidative stress
- A formula that includes essential vitamins like vitamin D and B vitamins to support energy production and overall health
- A product that is rich in minerals like calcium and zinc to support bone health and immune function
Choosing the Right Prenatal Vitamin
With so many prenatal vitamins available on the market, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. When selecting a prenatal vitamin, look for a product that is third-party tested, certified by a reputable organization, and contains a balanced blend of nutrients. Some key factors to consider include:
- A product that is free from artificial additives and allergens to minimize the risk of adverse reactions
- A prenatal vitamin that is specifically formulated for preconception to support the unique nutritional needs of women trying to conceive
- A product that is backed by scientific research and has a good reputation among healthcare providers and consumers
Is it okay to take prenatal vitamins when you're not pregnant?

Prenatal vitamins are dietary supplements designed to provide essential nutrients for pregnant women, but some individuals may consider taking them even when they’re not pregnant. The primary concern is whether these vitamins can provide benefits to non-pregnant individuals or if they pose potential risks.
Nutritional Benefits
Prenatal vitamins typically contain a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals, including folic acid, iron, and calcium. These nutrients can be beneficial for individuals who have deficiencies or are at risk of developing them. For example, individuals with a restrictive diet or certain medical conditions may benefit from taking prenatal vitamins. Some key benefits include:
- Addressing nutrient deficiencies that may be present due to a poor diet or certain medical conditions.
- Supporting overall health and well-being by providing essential vitamins and minerals.
- Helping to maintain healthy hair, nails, and skin due to the presence of biotin and other nutrients.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While prenatal vitamins can provide benefits, there are also potential risks to consider when taking them without being pregnant. One of the primary concerns is the risk of excessive intake of certain nutrients, such as iron and calcium. Some key considerations include:
- The risk of iron overload or toxicity due to excessive intake.
- The potential for interactions with other medications or exacerbating underlying medical conditions.
- The possibility of an imbalance of essential nutrients due to excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals.
Alternatives to Prenatal Vitamins
For individuals who are not pregnant but are considering taking prenatal vitamins, there may be alternative supplements or dietary changes that can provide the necessary nutrients. Some alternatives include:
- Taking a multivitamin specifically designed for non-pregnant individuals.
- Consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Addressing specific nutrient deficiencies through targeted supplements or dietary changes.
Do prenatal vitamins really help with pregnancy?
Prenatal vitamins are dietary supplements designed to provide essential nutrients to pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant. The primary goal of prenatal vitamins is to support the health of both the mother and the developing fetus during pregnancy. Research has shown that prenatal vitamins can play a crucial role in preventing birth defects, supporting fetal development, and maintaining the mother’s overall health.
Nutrients in Prenatal Vitamins
Prenatal vitamins typically contain a combination of vitamins and minerals, including folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are crucial for supporting the health of the mother and the developing fetus. Folic acid, for example, helps prevent neural tube defects, while iron supports the production of red blood cells.
- Folic acid is essential for preventing neural tube defects and supporting fetal development.
- Iron helps prevent anemia and supports the production of red blood cells.
- Calcium is crucial for fetal bone development and maintaining the mother’s bone health.
Benefits of Prenatal Vitamins
The benefits of prenatal vitamins are numerous, and research has shown that they can have a positive impact on pregnancy outcomes. Prenatal vitamins can help prevent birth defects, support fetal development, and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
- Prenatal vitamins can help prevent birth defects, such as neural tube defects and heart defects.
- They support fetal development, including brain and eye development.
- Prenatal vitamins can also help reduce the risk of pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia and gestational diabetes.
When to Start Taking Prenatal Vitamins
It is generally recommended that women start taking prenatal vitamins at least one month before becoming pregnant and continue taking them throughout pregnancy and breastfeeding. This can help ensure that the mother’s body has adequate stores of essential nutrients to support fetal development.
- Start taking prenatal vitamins at least one month before conception to support fetal development.
- Continue taking prenatal vitamins throughout pregnancy to support the health of the mother and fetus.
- Prenatal vitamins can also be beneficial during breastfeeding, as they support the mother’s overall health and milk production.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key nutrients in prenatal vitamins that support pregnancy wellness?
Prenatal vitamins contain a blend of essential nutrients that support the health and development of both the mother and the fetus. Folic acid is a crucial component, as it helps prevent birth defects of the brain and spine. Other key nutrients include iron, which supports the production of red blood cells, and calcium, which is essential for fetal bone development. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids support fetal brain and eye development, while vitamin D helps regulate calcium levels and support immune function.
Why are prenatal vitamins important for pregnant women?
Prenatal vitamins are vital for pregnant women as they help fill any nutritional gaps in their diet, ensuring that they and their developing fetus receive the necessary nutrients for optimal health. A well-balanced diet is essential, but prenatal vitamins provide additional support, particularly for women with dietary restrictions or preferences, such as vegetarians or vegans. By taking prenatal vitamins, women can reduce their risk of nutrient deficiencies and support a healthy pregnancy.
Can prenatal vitamins be taken during breastfeeding, and are they beneficial?
Yes, prenatal vitamins can be taken during breastfeeding, and they continue to provide benefits for both the mother and the baby. Breast milk is rich in nutrients, and prenatal vitamins help support the mother’s nutritional needs, ensuring that she can produce high-quality milk. Additionally, prenatal vitamins support the mother’s overall health and postpartum recovery, helping her to replenish iron stores and maintain energy levels.
How should I choose the right prenatal vitamin for my pregnancy?
When selecting a prenatal vitamin, it’s essential to consider the quality and purity of the product. Look for a prenatal vitamin that contains the recommended amounts of folic acid, iron, and calcium. Also, consider a product that is third-party tested and certified by a reputable organization, such as the NSF International or the National Science Foundation. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best prenatal vitamin for your individual needs and health status.