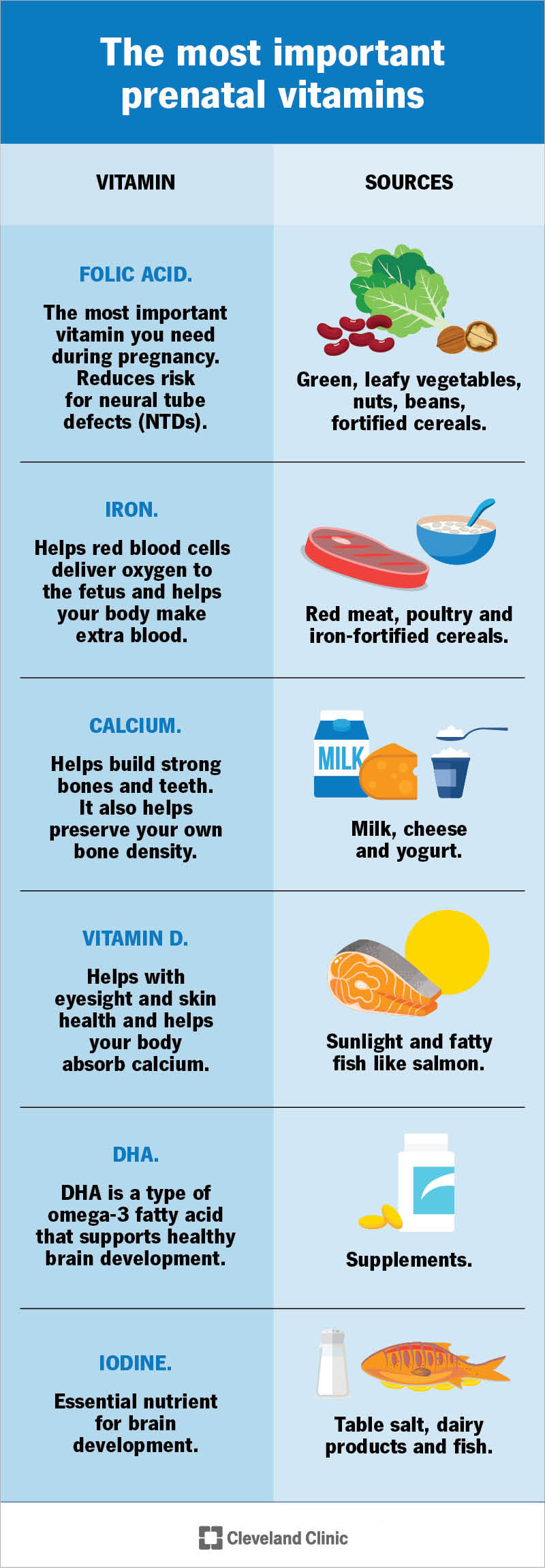
During pregnancy, it’s crucial for women to be mindful of their nutrient intake to support their health and the development of their baby. While prenatal vitamins are recommended, not all supplements are safe for pregnant women. Certain vitamins and minerals can pose risks when taken in high doses. Understanding which pregnancy vitamins to avoid is essential to prevent potential harm. Excessive intake of specific nutrients can lead to complications, highlighting the need for careful consideration of dietary supplements during this critical period. Safety should be the top priority.

Pregnancy Vitamins to Avoid for Safety: Understanding the Risks
When it comes to pregnancy, it’s crucial for expectant mothers to be mindful of their vitamin intake to ensure the health and safety of both themselves and their developing baby. While vitamins are essential for maintaining good health, some can pose risks during pregnancy. Understanding which pregnancy vitamins to avoid is vital for a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Vitamin A: The Risks of Excessive Intake
Vitamin A is crucial for health, but excessive intake, particularly in its retinol form, can lead to birth defects. High doses of Vitamin A have been associated with an increased risk of miscarriage and fetal abnormalities. Pregnant women should limit their intake of Vitamin A-rich foods and avoid supplements that contain retinol.
| Vitamin A Sources | Safe Intake |
|---|---|
| Retinol supplements | Avoid during pregnancy |
| Liver and liver products | Limit consumption |
| Fish liver oils | Avoid unless advised by a healthcare provider |
The Safety Concerns of High-Dose Vitamin C
While Vitamin C is generally considered safe and is important for immune function, high doses can cause gastrointestinal disturbances. Although rare, excessive intake can potentially lead to more serious issues. Pregnant women should be cautious with high-dose Vitamin C supplements.
| Vitamin C Intake | Recommended Daily Amount |
|---|---|
| Food sources like citrus fruits and strawberries | 85 mg per day |
| Supplements | Not recommended above 2000 mg per day |
Vitamin E: Understanding the Risks of High Intake
Vitamin E is known for its antioxidant properties, but high doses have been linked to an increased risk of bleeding. During pregnancy, it’s essential to be mindful of Vitamin E intake to avoid any potential complications.
| Vitamin E Sources | Recommended Intake |
|---|---|
| Nuts and seeds | 15 mg per day |
| Vegetable oils | Consume in moderation |
| Supplements | Avoid high doses unless medically advised |
Potential Dangers of Excessive Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is important for many bodily functions, but excessive intake can cause nerve damage. Pregnant women should be aware of their Vitamin B6 intake to prevent any adverse effects.
| Vitamin B6 Sources | Safe Upper Limit |
|---|---|
| Food sources like fish, eggs, and chickpeas | 1.9 mg per day for pregnant women |
| Supplements | Not to exceed 100 mg per day |
Herbal and Unregulated Supplements: Proceed with Caution
Some herbal supplements and unregulated products can contain harmful substances that are not safe during pregnancy. It’s crucial for pregnant women to consult with their healthcare provider before taking any supplement.
| Supplement Type | Pregnancy Safety |
|---|---|
| Unregulated or herbal supplements | Generally not recommended |
| Regulated prenatal vitamins | Safe when taken as directed |
What vitamins should you not take when trying to get pregnant?
When trying to conceive, it’s essential to be mindful of the vitamins and supplements you’re taking, as some can have adverse effects on fertility or fetal development. Certain vitamins and supplements can interfere with conception or cause harm to the developing fetus.
Vitamins to Limit or Avoid During Conception
Some vitamins and supplements should be limited or avoided when trying to get pregnant due to their potential to cause harm. High doses of vitamin A, for example, have been linked to an increased risk of birth defects. It’s crucial to be aware of the vitamins and supplements that can negatively impact fertility or fetal development.
- Vitamin A: High doses can cause birth defects, so it’s recommended to limit intake to 10,000 IU or less per day.
- Excessive Vitamin C: High doses may cause an imbalance in the body’s natural processes, potentially affecting fertility.
- Unregulated Herbal Supplements: Some herbal supplements can interact with other medications or have adverse effects on fertility or fetal development.
Potential Risks Associated with Certain Vitamins
Certain vitamins and supplements can pose risks during conception, and it’s crucial to understand these risks to make informed decisions. Uncontrolled intake of certain nutrients can lead to imbalances or adverse effects.
- High-dose vitamin B6: Excessive intake can cause neurological symptoms and potentially affect fertility.
- Excessive intake of iron: While iron is essential, excessive intake can cause constipation, nausea, and potentially harm the developing fetus.
- Misuse of fat-soluble vitamins: Vitamins like A, D, E, and K can accumulate in the body and cause toxicity if taken in excess.
Precautions for Safe Supplementation
When trying to conceive, it’s essential to take a thoughtful and informed approach to supplementation. Consulting a healthcare provider before taking any vitamins or supplements is crucial to ensure safe and effective use.
- Folic acid supplementation: Folic acid is recommended for pregnant women to prevent birth defects, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for the correct dosage.
- Choose regulated products: Opt for supplements from reputable manufacturers that adhere to regulatory standards.
- Monitor intake and adjust as needed: Regularly review your supplement regimen with a healthcare provider to ensure it remains safe and effective.
What vitamin A products to avoid during pregnancy?

During pregnancy, it’s crucial to be cautious with the intake of vitamin A products due to the potential risk of birth defects. High levels of vitamin A, particularly in its retinol form, can be harmful to the developing fetus. Therefore, pregnant women or those planning to conceive should be aware of the products that contain high levels of vitamin A or its derivatives.
Products Containing Retinol to Avoid
Pregnant women should avoid skincare and cosmetic products that contain retinol or its derivatives, such as retinyl palmitate, retinyl acetate, and retinyl linoleate, as these can be absorbed into the bloodstream and potentially harm the fetus.
- Anti-aging creams that contain retinol for their regenerative properties.
- Acne treatments that use retinoids to reduce acne and prevent future breakouts.
- Some cosmetic serums designed to reduce fine lines and wrinkles.
Vitamin A Supplements and Their Risks
It’s also important for pregnant women to be cautious with dietary supplements. Vitamin A supplements, especially those in high doses, should be avoided unless specifically recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Fish liver oil supplements, which are rich in vitamin A.
- Multivitamins that contain more than the recommended daily intake of vitamin A.
- Any supplement labeled as containing retinol or its derivatives.
Safe Alternatives for Pregnant Women
While avoiding products with high vitamin A content, pregnant women can still maintain a healthy skincare routine and support their nutritional needs with safer alternatives.
- Using skincare products with natural ingredients that are known to be safe during pregnancy.
- Opting for prenatal vitamins that are formulated to meet the nutritional needs of pregnant women without exceeding safe levels of vitamin A.
- Choosing beta-carotene supplements, which are considered safer as they are converted to vitamin A in the body as needed.
Which vitamin poses a risk of toxicity during pregnancy?

The vitamin that poses a risk of toxicity during pregnancy is Vitamin A. High levels of Vitamin A can cause teratogenic effects, leading to birth defects. It is crucial for pregnant women to be aware of the risks associated with excessive intake of this vitamin.
Understanding Vitamin A Toxicity
Vitamin A toxicity occurs when there is an excessive intake of retinol, a form of Vitamin A found in animal products and supplements. This can happen through consuming high amounts of liver, liver products, or taking retinoid supplements. The risk is particularly high during the early stages of pregnancy when the fetus is most vulnerable to teratogenic effects.
- Birth defects: High levels of Vitamin A have been linked to an increased risk of birth defects, including craniofacial abnormalities and central nervous system defects.
- Pregnancy complications: Excessive Vitamin A intake may also lead to pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage and preterm labor.
- Fetal development issues: The teratogenic effects of Vitamin A can result in issues with fetal development, affecting the overall health and well-being of the newborn.
Sources of Vitamin A and Risks
Preformed Vitamin A (retinol) is found in animal products like liver, fish liver oil, and dairy products, as well as in supplements. Pregnant women should be cautious about consuming these products in excess.
- Liver and liver products: These are particularly high in Vitamin A and should be avoided or consumed in very limited amounts during pregnancy.
- Retinoid supplements: Pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant should avoid taking retinoid supplements unless advised by a healthcare provider.
- Fortified foods: Some foods are fortified with Vitamin A, and while they are generally safe, pregnant women should still be mindful of their overall Vitamin A intake.
Safely Managing Vitamin A Intake During Pregnancy
To minimize the risk of Vitamin A toxicity, pregnant women should be aware of their Vitamin A intake from all sources, including diet and supplements.
- Consult a healthcare provider: Before taking any supplements, pregnant women should consult with a healthcare provider to ensure they are not at risk of excessive Vitamin A intake.
- Choose safe food sources: Opting for beta-carotene rich foods like fruits and vegetables is a safer way to meet Vitamin A needs, as beta-carotene is converted to Vitamin A in the body as needed and is not associated with the same level of toxicity risk.
- Monitor overall diet: Being mindful of the overall diet and avoiding excessive consumption of foods high in preformed Vitamin A can help mitigate the risk of toxicity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the potential risks of taking certain pregnancy vitamins?
Taking certain pregnancy vitamins can pose significant risks to the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Some vitamins, when taken in high doses, can be toxic or cause adverse reactions. For instance, excessive intake of vitamin A can lead to birth defects, while too much iron can cause gastrointestinal issues. It is essential to be aware of these risks to ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Which pregnancy vitamins should be avoided or limited during pregnancy?
Certain pregnancy vitamins should be avoided or limited during pregnancy due to their potential to cause harm. Vitamin A supplements, for example, should be limited to avoid teratogenic effects. Similarly, high doses of iron can cause constipation, nausea, and vomiting. Additionally, some prenatal vitamins may contain herbal ingredients that are not recommended during pregnancy, such as St. John’s Wort, which can interact with other medications.
How can I identify safe pregnancy vitamins?
To identify safe pregnancy vitamins, it is crucial to carefully read the label and look for products that are specifically formulated for pregnant women. Check the ingredient list for essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, and calcium, and avoid products with unnecessary additives or high doses of certain vitamins. Also, opt for products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to good manufacturing practices.
Can I consult my healthcare provider before taking pregnancy vitamins?
It is highly recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any pregnancy vitamins. They can help determine the best course of prenatal nutrition and recommend safe and effective supplements based on individual needs. A healthcare provider can also provide guidance on dosage and potential interactions with other medications, ensuring a healthy and safe pregnancy.