Expecting a baby is an exciting time, and maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for the health and development of the unborn child. However, getting all the necessary nutrients through food alone can be challenging. This is where prenatal multivitamins come into play, helping fill any nutritional gaps. With numerous options available, choosing the right prenatal multivitamin can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about prenatal multivitamins, from their importance and benefits to key ingredients and selection tips, ensuring you make an informed decision for a healthy pregnancy.

Understanding the Importance of Prenatal Multivitamins
Prenatal multivitamins are dietary supplements designed to provide essential nutrients to pregnant women or those planning to conceive. These supplements play a crucial role in supporting the health and development of both the mother and the fetus during pregnancy. A well-balanced prenatal multivitamin can help fill any nutritional gaps in the mother’s diet, ensuring that she and her baby receive the necessary vitamins and minerals for optimal health.
Key Ingredients in Prenatal Multivitamins
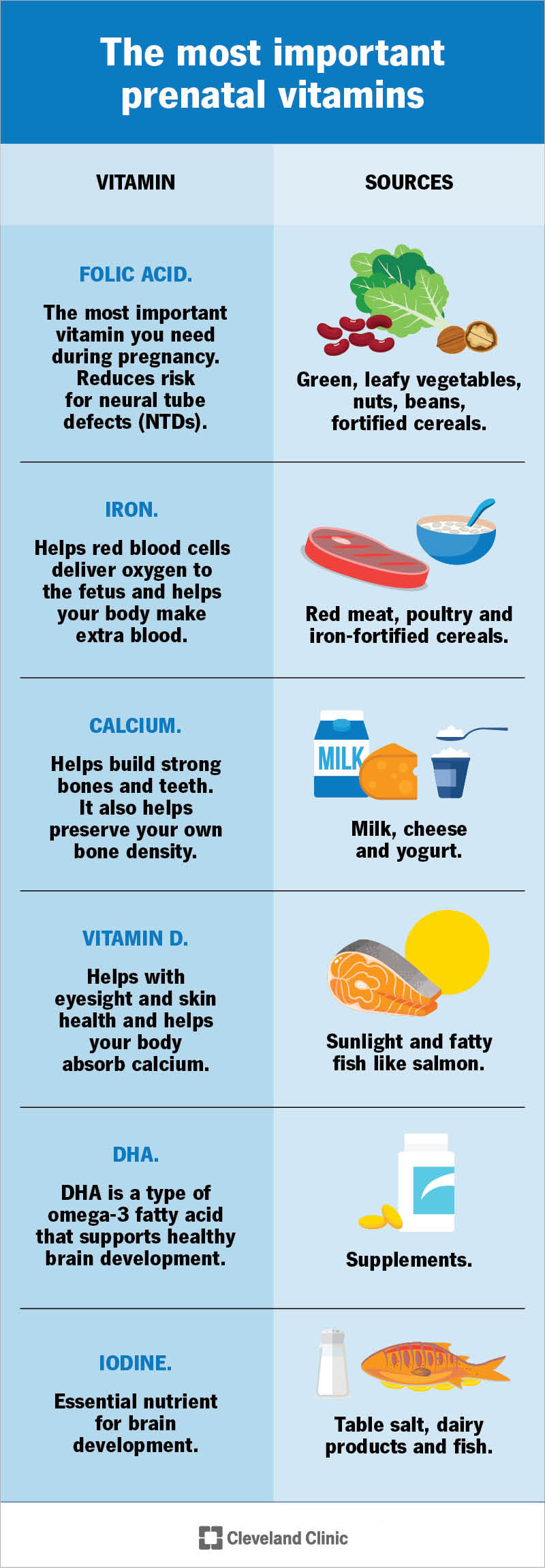
Prenatal multivitamins typically contain a blend of vitamins and minerals that are vital for fetal development and maternal health. Some of the key ingredients include folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Folic acid is crucial for preventing birth defects of the brain and spine, while iron supports the production of red blood cells. Calcium is essential for the development of the baby’s bones, teeth, and muscles, and omega-3 fatty acids support fetal brain development.
| Nutrient | Importance | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Folic Acid | Prevents birth defects of the brain and spine | 600-800 mcg |
| Iron | Supports red blood cell production | 27 mg |
| Calcium | Essential for fetal bone development | 1,000 mg |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Supports fetal brain development | 200-300 mg |
Benefits of Taking Prenatal Multivitamins
Taking a prenatal multivitamin can have numerous benefits for pregnant women. These supplements can help prevent birth defects, support fetal development, and alleviate morning sickness. Additionally, prenatal multivitamins can help manage fatigue and support overall maternal health.
How to Choose the Right Prenatal Multivitamin
With so many prenatal multivitamins available on the market, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. When selecting a prenatal multivitamin, look for a product that contains the essential nutrients mentioned earlier, such as folic acid and iron. Also, consider a product that is third-party tested and has a reputable manufacturer.
Potential Side Effects of Prenatal Multivitamins
While prenatal multivitamins are generally considered safe, some women may experience gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or constipation. To minimize these effects, it’s recommended to take the supplement with food or switch to a different product if the side effects persist.
When to Start Taking Prenatal Multivitamins
It’s recommended to start taking prenatal multivitamins at least one month before conception to ensure that the body has adequate stores of essential nutrients. Continuing to take a prenatal multivitamin throughout pregnancy and lactation can also support maternal and fetal health.
How do I know which prenatal vitamins to take?

To determine the most suitable prenatal vitamins for your needs, it’s essential to consider several factors, including your dietary habits, health status, and the specific nutrients contained in the supplement.
Understanding Prenatal Vitamin Composition
Prenatal vitamins are dietary supplements designed to provide essential nutrients crucial for a healthy pregnancy. They typically contain a mix of vitamins and minerals, including folic acid, iron, and calcium. When selecting a prenatal vitamin, it’s crucial to examine the ingredient list to ensure it contains the necessary nutrients.
- Folic acid is critical for preventing birth defects of the baby’s brain and spine.
- Iron supports the mother’s increased blood volume and the baby’s growth.
- Calcium is vital for the development of the baby’s bones, teeth, and muscles.
Assessing Your Dietary Needs
Your dietary habits play a significant role in determining the right prenatal vitamin for you. If you have a restricted diet or certain nutritional deficiencies, you may require a prenatal vitamin that is formulated to address these specific needs. For example, if you’re vegan or vegetarian, you might need a prenatal vitamin that contains vitamin B12, as this vitamin is primarily found in animal products.
- Evaluate your typical daily food intake to identify potential nutritional gaps.
- Consider consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to assess your nutritional needs.
- Look for prenatal vitamins that are fortified with additional nutrients if necessary, such as omega-3 fatty acids for fetal brain development.
Choosing the Right Prenatal Vitamin Brand
With numerous prenatal vitamin brands available, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. It’s essential to opt for a reputable brand that adheres to good manufacturing practices (GMPs) and third-party testing.
- Research the brand’s reputation and read reviews from other pregnant women.
- Check if the product is certified by a third-party organization, such as NSF International or ConsumerLab.com.
- Ensure the product is manufactured in a facility that follows GMPs to guarantee quality and purity.
What is the recommendation for the need for multivitamin supplements during pregnancy?

The recommendation for the need for multivitamin supplements during pregnancy is a topic of ongoing debate among healthcare professionals. The general consensus is that a well-balanced diet should provide all the necessary nutrients for a healthy pregnancy. However, due to various factors such as dietary restrictions, socioeconomic status, and certain medical conditions, some pregnant women may require additional nutritional support.
Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s body requires increased amounts of essential nutrients to support the growth and development of the fetus. These nutrients include folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. A multivitamin supplement can help fill any nutritional gaps in the diet. The key nutritional needs during pregnancy are:
- Folic acid to prevent neural tube defects
- Iron to support the production of red blood cells
- Calcium to promote fetal bone development
Benefits of Multivitamin Supplements
Multivitamin supplements can provide numerous benefits for pregnant women, particularly those with restricted diets or certain medical conditions. These benefits include reduced risk of birth defects, improved fetal development, and enhanced maternal health. Some of the key benefits of multivitamin supplements during pregnancy are:
- Prevention of micronutrient deficiencies that can lead to complications during pregnancy
- Support for fetal development through the provision of essential nutrients
- Improved maternal health outcomes through the prevention of pregnancy-related complications
Guidelines for Multivitamin Supplementation
The guidelines for multivitamin supplementation during pregnancy vary depending on individual circumstances. Pregnant women should consult with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. The key considerations for multivitamin supplementation during pregnancy are:
- Individual nutritional needs based on dietary habits and medical history
- Type and quality of multivitamin supplement to ensure it meets prenatal nutritional requirements
- Dosage and duration of supplementation to minimize the risk of adverse effects
What should you not take with prenatals?
When taking prenatal vitamins, it’s essential to be aware of the substances that should not be taken concurrently, as they may interact with the vitamins or exacerbate certain health conditions.
Medications to Avoid with Prenatals
Certain medications can interact with prenatal vitamins, reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of adverse effects. For instance, antibiotics such as tetracycline and fluoroquinolones can chelate minerals like iron and calcium found in prenatal vitamins, thereby reducing their absorption.
- Tetracycline antibiotics should be taken on an empty stomach, and their absorption can be affected by the calcium in prenatal vitamins.
- Antacids containing aluminum, magnesium, or calcium can also interfere with the absorption of certain minerals in prenatal vitamins.
- Blood thinners like warfarin may be affected by the vitamin K in prenatal vitamins, potentially altering their efficacy.
Supplements to Avoid with Prenatals
Taking certain supplements alongside prenatal vitamins can lead to excessive intake of specific nutrients or interact with the vitamins. For example, taking additional iron supplements with prenatal vitamins can lead to iron overload.
- Extra calcium supplements may increase the risk of kidney stone formation and interact with the absorption of other minerals.
- High doses of vitamin A can be teratogenic and should be avoided during pregnancy, making it crucial to monitor total vitamin A intake from all sources.
- Mineral supplements like zinc and copper should be taken with caution, as excessive intake can lead to imbalances.
Substances to Limit with Prenatals
Some substances, while not necessarily contraindicated with prenatal vitamins, should be consumed in moderation to avoid adverse effects. For example, excessive intake of caffeine can increase the risk of miscarriage and growth restriction.
- Caffeine intake should be limited to less than 200 mg per day to minimize risks during pregnancy.
- Alcohol consumption should be avoided altogether due to its potential to cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
- Certain herbal teas or supplements may interact with prenatal vitamins or have adverse effects on pregnancy outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential nutrients in a complete prenatal multivitamin?
A complete prenatal multivitamin should contain a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals that support the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Key nutrients include folic acid, which prevents birth defects of the brain and spine, iron, which supports the mother’s increased blood volume and prevents anemia, calcium, which is crucial for fetal bone development, and omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, which supports fetal brain and eye development. Additionally, vitamin D is important for bone health and immune function. A well-formulated prenatal multivitamin ensures that the mother and fetus receive these essential nutrients.
How does a prenatal multivitamin support fetal development?
A prenatal multivitamin plays a critical role in supporting fetal development by providing the necessary building blocks for growth. Folic acid is particularly important in the early stages of pregnancy for preventing neural tube defects. As the pregnancy progresses, other nutrients like iron and calcium become crucial for supporting the mother’s health and the baby’s development. Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, support the development of the baby’s brain and eyes. A prenatal multivitamin helps fill any nutritional gaps in the mother’s diet, ensuring that the fetus receives the necessary nutrients for optimal development.
Can a prenatal multivitamin help alleviate pregnancy symptoms?
While a prenatal multivitamin is primarily taken to support the health of the mother and fetus, it can also help alleviate some pregnancy symptoms. For example, iron can help reduce the severity of anemia, which is common during pregnancy and can cause fatigue and weakness. Some prenatal multivitamins contain additional ingredients that may help with morning sickness or other symptoms. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplement, especially if you’re experiencing severe symptoms.
Are there any differences in prenatal multivitamins that I should be aware of?
Yes, there are significant differences in prenatal multivitamins that you should be aware of. Some prenatal multivitamins may contain higher levels of certain nutrients, such as folic acid or iron, while others may include additional ingredients like probiotics or antioxidants. The quality of the ingredients and the manufacturing process can also vary between brands. It’s crucial to choose a prenatal multivitamin that is manufactured by a reputable company and has been tested for purity and potency. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best prenatal multivitamin for your specific needs.