Folic acid is a crucial nutrient for pregnant women, playing a vital role in preventing birth defects of the brain and spine. With numerous supplements available, selecting the best folic acid for pregnancy can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the importance of folic acid during pregnancy, recommended dosages, and key factors to consider when choosing a supplement. By understanding the benefits and options, expectant mothers can make informed decisions to support a healthy pregnancy and fetal development, ensuring the best possible start for their baby. Proper supplementation is essential.

Understanding the Importance of Folic Acid During Pregnancy
Folic acid is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in preventing birth defects of the brain and spine. It is a form of vitamin B9, which is essential for the production of red blood cells and the prevention of anemia. During pregnancy, the demand for folic acid increases due to the rapid growth and development of the fetus. A deficiency in folic acid can lead to serious health complications for both the mother and the baby.
Benefits of Folic Acid for Pregnant Women
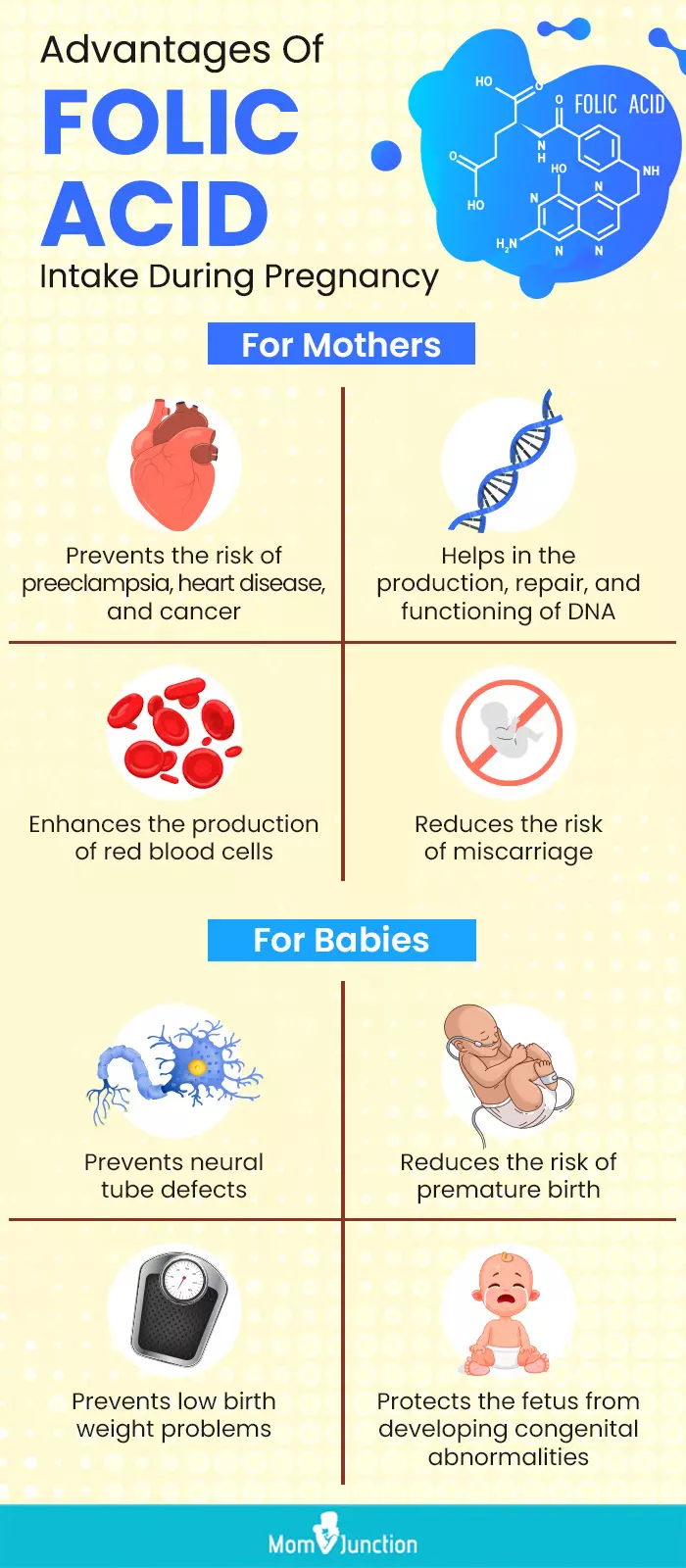
Folic acid supplements have been shown to have numerous benefits for pregnant women. Some of the key advantages include: – Prevention of Neural Tube Defects (NTDs): Folic acid helps prevent NTDs, such as spina bifida and anencephaly, which occur when the neural tube does not close properly. – Reducing the Risk of Miscarriage: Studies have found that folic acid supplementation can reduce the risk of miscarriage. – Lowering the Risk of Preterm Labor: Folic acid has been linked to a reduced risk of preterm labor and low birth weight.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevention of NTDs | Folic acid prevents birth defects of the brain and spine. |
| Reducing Miscarriage Risk | Folic acid supplementation reduces the risk of miscarriage. |
| Lowering Preterm Labor Risk | Folic acid is associated with a reduced risk of preterm labor. |
Recommended Daily Intake of Folic Acid for Pregnant Women
The recommended daily intake of folic acid for pregnant women varies by health organization, but most recommend at least 600 to 800 micrograms (mcg) per day. It is essential to consume folic acid through a combination of diet and supplements to meet this daily requirement.
Food Sources Rich in Folic Acid
While supplements are crucial, dietary sources of folic acid are also vital. Foods rich in folate include: – Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are high in folate. – Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources. – Citrus Fruits: Oranges and orange juice are good sources of folate.
| Food | Folate Content (mcg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Spinach (cooked) | 262 |
| Lentils (cooked) | 358 |
| Orange Juice | 74 |
Choosing the Best Folic Acid Supplement for Pregnancy
When selecting a folic acid supplement, it is crucial to consider the form of folate used. Methylfolate is a more bioavailable form that some women may prefer, especially those with certain genetic variations affecting folate metabolism.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Folic Acid Supplements
While generally safe, high doses of folic acid can mask vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms. Pregnant women should be aware of the potential risks and consult their healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Masking B12 Deficiency | High doses of folic acid can hide B12 deficiency symptoms. |
| Interaction with Medications | Folic acid can interact with certain medications. |
Consulting a Healthcare Provider Before Taking Folic Acid
It is essential for pregnant women to consult their healthcare provider before starting folic acid supplements. The provider can recommend the appropriate dosage and monitor for any potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
What is the most recommended folic acid for pregnancy?

The most recommended folic acid for pregnancy is a crucial nutrient that prevents birth defects of the baby’s brain and spine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that all women of childbearing age take 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid daily, starting at least one month before becoming pregnant and continuing through the first trimester of pregnancy.
Benefits of Folic Acid During Pregnancy
Folic acid is essential for the prevention of Neural Tube Defects (NTDs), such as spina bifida and anencephaly. These defects occur when the neural tube, which forms the brain and spine, does not close properly during fetal development. The benefits of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy are well-documented, and include:
- Prevention of NTDs: Folic acid has been shown to reduce the risk of NTDs by up to 70%.
- Reduced risk of other birth defects: Some studies suggest that folic acid may also reduce the risk of other birth defects, such as heart defects and cleft palate.
- Support for fetal development: Folic acid is necessary for the production of red blood cells and the synthesis of DNA, making it essential for fetal growth and development.
Recommended Forms of Folic Acid
There are several forms of folic acid available, including prenatal vitamins, folic acid supplements, and fortified foods. Prenatal vitamins typically contain a range of essential nutrients, including folic acid, iron, and calcium. Folic acid supplements are available in various strengths, including 400 mcg and 800 mcg. Fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals and bread, may also contain folic acid. When choosing a folic acid supplement, consider the following:
- Look for a supplement with 400 mcg of folic acid: This is the recommended daily dose for pregnant women.
- Check the ingredient label: Ensure that the supplement contains folate or 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), which are more easily absorbed by the body than synthetic folic acid.
- Consult with a healthcare provider: Before taking any supplement, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your individual needs.
Food Sources of Folic Acid
In addition to supplements, folic acid can be obtained through a balanced diet that includes folate-rich foods. Some examples of folate-rich foods include:
- Dark leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are all rich in folate.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are all good sources of folate.
- Fortified cereals: Many breakfast cereals are fortified with folic acid, making them a convenient and easy way to boost your intake.
Which company folic acid is best for pregnancy?

When considering the best folic acid supplement for pregnancy, several factors come into play, including the product’s quality, the manufacturer’s reputation, and the specific formulation that meets the pregnant individual’s needs. One of the most recognized and trusted brands for prenatal supplements, including folic acid, is Nature’s Bounty. Their products are often praised for their high quality and adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMPs). Another reputable brand is Garden of Life, known for its organic and non-GMO products, including folate supplements that are crucial during pregnancy.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Folic Acid Supplement
Choosing the right folic acid supplement during pregnancy involves several key considerations to ensure the product is both safe and effective. Purity and potency are crucial, as they directly impact the supplement’s efficacy. It’s also important to consider the presence of additional nutrients that complement folic acid, such as iron and other B vitamins, which are vital for a healthy pregnancy. A well-rounded prenatal supplement should support overall maternal health and fetal development.
- Ensure the product is manufactured by a company that follows GMPs to guarantee quality and purity.
- Opt for a supplement that contains the recommended daily intake of 400 to 800 micrograms of folic acid for pregnant women.
- Consider a product that is also rich in other essential nutrients for pregnancy, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin D.
Benefits of Folic Acid Supplements During Pregnancy
Folic acid is a critical nutrient during pregnancy due to its role in preventing neural tube defects (NTDs) in the developing fetus. NTDs are serious birth defects of the brain and spine. Taking folic acid before and during early pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of these conditions. Moreover, folic acid supports the overall health of the mother and fetus by contributing to the production of red blood cells and preventing anemia.
- Folic acid helps prevent NTDs such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
- It supports the production of red blood cells, reducing the risk of anemia in the mother.
- Folic acid is also involved in the synthesis of DNA, crucial for the rapid cell division during fetal development.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While folic acid is generally considered safe when taken as directed, there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of, particularly with high doses. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea or abdominal cramps. It’s also important to be aware of the risk of masking a vitamin B12 deficiency with high doses of folic acid, as it can lead to neurological damage if left untreated.
- High doses of folic acid can mask a vitamin B12 deficiency, potentially leading to neurological problems.
- Some people may experience gastrointestinal upset, including nausea or abdominal pain.
- It’s essential to follow the recommended dosage to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Is 1000 mcg of folic acid too much when pregnant?
The recommended daily intake of folic acid for pregnant women is typically around 600-800 mcg. However, some prenatal vitamins and supplements may contain up to 1000 mcg of folic acid. The safety of taking 1000 mcg of folic acid during pregnancy is a topic of ongoing debate.
Folic Acid and Pregnancy: Understanding the Risks
Taking high doses of folic acid during pregnancy may pose certain risks. While folic acid is essential for preventing birth defects of the brain and spine, excessive intake may mask a vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to neurological problems. Some studies have also raised concerns about the potential link between high folic acid intake and an increased risk of certain health issues.
- Masking Vitamin B12 Deficiency: High doses of folic acid can mask the symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency, potentially leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Potential Link to Health Issues: Some research suggests a possible link between high folic acid intake and an increased risk of certain health issues, such as autism and cancer.
- Importance of Balanced Intake: It is crucial to strike a balance between getting enough folic acid to prevent birth defects and avoiding excessive intake that may pose risks.
Benefits of Folic Acid During Pregnancy
Folic acid is a crucial nutrient during pregnancy, playing a vital role in preventing birth defects of the brain and spine. Adequate folic acid intake has been shown to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) such as spina bifida and anencephaly. The benefits of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy are well-established, and most healthcare providers recommend taking a prenatal vitamin containing folic acid.
- Prevention of Neural Tube Defects: Folic acid supplementation has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of NTDs.
- Importance of Early Supplementation: Folic acid is most effective in preventing NTDs when taken before and during early pregnancy.
- Recommended Daily Intake: Pregnant women should aim to consume 600-800 mcg of folic acid per day through a combination of diet and supplements.
Guidelines for Safe Folic Acid Supplementation
To ensure safe folic acid supplementation during pregnancy, it is essential to follow the guidelines recommended by healthcare providers. Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking any supplements, especially if they have a history of medical conditions or are taking medications.
- Consult Healthcare Provider: Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking any supplements or making changes to their diet.
- Choose Reputable Brands: When selecting a prenatal vitamin or folic acid supplement, choose reputable brands that adhere to quality standards.
- Monitor Intake and Health: Pregnant women should monitor their folic acid intake and overall health, reporting any concerns or side effects to their healthcare provider.
Which form of folate is best for pregnancy?

The most effective form of folate for pregnancy is L-Methylfolate or 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF), as it is the biologically active form of folate that can be directly utilized by the body. Unlike synthetic folic acid, L-Methylfolate does not require conversion by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, making it more suitable for individuals with certain genetic variations that affect folate metabolism.
Folate Forms and Their Significance
Folate is a crucial nutrient during pregnancy, playing a vital role in preventing neural tube defects (NTDs) such as spina bifida and anencephaly. The different forms of folate have varying levels of bioavailability and effectiveness.
- The synthetic form, folic acid, is commonly found in prenatal supplements and fortified foods but requires enzymatic conversion to become active.
- L-Methylfolate is directly usable by the body, bypassing the need for this conversion, making it particularly beneficial for women with MTHFR gene mutations.
- Other forms like folinic acid are also used, especially in cases where there’s a need for rapid folate supplementation.
Benefits of L-Methylfolate in Pregnancy
L-Methylfolate is particularly beneficial during pregnancy due to its high bioavailability and the critical role it plays in fetal development. It supports the prevention of NTDs and is involved in various bodily processes, including DNA synthesis and repair.
- Prevention of Neural Tube Defects: L-Methylfolate is directly involved in the prevention of NTDs by ensuring adequate folate levels during early pregnancy.
- Supports Fetal Development: Beyond NTD prevention, L-Methylfolate is essential for overall fetal development and maternal health.
- Genetic Considerations: For women with genetic mutations affecting folate metabolism, such as MTHFR mutations, L-Methylfolate is especially recommended.
Choosing the Right Folate Supplement
When selecting a folate supplement during pregnancy, it’s essential to consider the form of folate and individual health needs.
- Consult Healthcare Provider: It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best form and dosage of folate based on individual health status and genetic factors.
- Look for Bioavailable Forms: Opting for supplements containing L-Methylfolate or other bioavailable forms can be more effective.
- Combination Supplements: Some prenatal vitamins combine folate with other essential nutrients, supporting overall maternal and fetal health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recommended daily intake of folic acid during pregnancy?
The recommended daily intake of folic acid during pregnancy is crucial for preventing birth defects of the baby’s brain and spine. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that all women of childbearing age take 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid daily, and pregnant women take 600-800 mcg daily. This essential nutrient helps prevent neural tube defects (NTDs), such as spina bifida and anencephaly. It is vital to consume the recommended amount of folic acid before and during pregnancy to ensure the healthy development of the fetus.
What are the best sources of folic acid for pregnant women?
Pregnant women can obtain folic acid from various food sources and supplements. Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are rich in folate, the natural form of folic acid. Other folate-rich foods include legumes, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals. However, it can be challenging to get enough folic acid from diet alone, making prenatal supplements a reliable option. When choosing a prenatal supplement, look for one that contains methylfolate or folinic acid, as these forms are more easily absorbed by the body.
Can I take too much folic acid during pregnancy?
While folic acid is essential during pregnancy, excessive intake can have negative effects. Taking more than 1,000 mcg of folic acid daily can mask a vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to neurological problems. High doses of folic acid may also interact with certain medications, such as anticonvulsants. It is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
How does folic acid prevent birth defects during pregnancy?
Folic acid plays a critical role in preventing neural tube defects (NTDs) by helping to close the neural tube, which forms the brain and spine, early in fetal development. When the neural tube fails to close properly, NTDs occur. Adequate folic acid intake before and during pregnancy reduces the risk of NTDs by ensuring the proper closure of the neural tube. Research has shown that folic acid supplementation can reduce the risk of NTDs by up to 70%.














