The relationship between vitamin D and testosterone has garnered significant attention in recent years, as research continues to unveil the intricate connections between these two vital components of overall health. Testosterone, a crucial hormone for both men and women, plays a key role in regulating various bodily functions, while vitamin D is essential for bone health and immune function. Emerging evidence suggests a link between vitamin D levels and testosterone production, sparking interest in the potential benefits of maintaining adequate vitamin D levels for optimal testosterone health and overall wellbeing.

The Relationship Between Vitamin D and Testosterone Levels
The connection between Vitamin D and testosterone has been a subject of interest in the medical community for several years. Research has shown that there is a significant correlation between the levels of Vitamin D in the body and the production of testosterone. Testosterone is a crucial hormone in the human body, responsible for a range of functions including muscle mass, bone density, and sex drive. Vitamin D, on the other hand, is essential for maintaining strong bones, immune function, and overall health. Understanding the link between these two is vital for maintaining optimal health.
The Role of Vitamin D in Testosterone Production
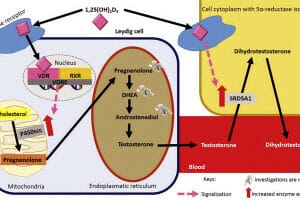
Studies have indicated that Vitamin D plays a significant role in the production of testosterone. The mechanism behind this involves the regulation of gene expression that is crucial for testosterone synthesis. When Vitamin D levels are adequate, it is believed to support the health of the Leydig cells in the testes, which are responsible for producing testosterone.
| Vitamin D Level | Testosterone Level |
|---|---|
| Deficient | Low |
| Insufficient | Borderline |
| Sufficient | Normal/Optimal |
Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on Testosterone Levels
A deficiency in Vitamin D has been associated with lower levels of testosterone. This is concerning because low testosterone can lead to a variety of health issues, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and reduced muscle mass and bone density. Ensuring adequate levels of Vitamin D through sun exposure, diet, or supplementation is crucial for maintaining healthy testosterone levels.
Mechanisms Behind the Vitamin D and Testosterone Connection
The exact mechanisms behind how Vitamin D influences testosterone production are still under investigation. However, it is known that Vitamin D receptors are present in the Leydig cells, suggesting a direct role in testosterone synthesis. Moreover, Vitamin D is thought to influence the expression of genes involved in testosterone production.
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D Receptors | Presence in Leydig cells indicates a role in testosterone synthesis |
| Gene Expression | Regulation of genes crucial for testosterone production |
Supplementation and Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Vitamin D and Testosterone
For individuals with deficiencies or insufficiencies in Vitamin D and testosterone, supplementation and lifestyle changes can be beneficial. Increasing Vitamin D through supplements or by spending more time outdoors can help boost testosterone levels. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and ensuring adequate sleep are lifestyle modifications that can support both Vitamin D and testosterone health.
| Lifestyle Change | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Outdoor Activities | Boosts Vitamin D levels |
| Regular Exercise | Supports testosterone production |
| Healthy Diet | Provides essential nutrients for Vitamin D and testosterone |
Monitoring and Maintaining Optimal Vitamin D and Testosterone Levels
Regular monitoring of Vitamin D and testosterone levels is essential for early detection of any imbalances. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on testing and interpreting results. Maintaining optimal levels of both Vitamin D and testosterone is key to preventing a range of health issues and ensuring overall well-being.
| Parameter | Optimal Range |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D | 30-50 ng/mL |
| Testosterone | 500-1000 ng/dL for adult men |
What is the relationship between vitamin D and testosterone?
![]()
The relationship between vitamin D and testosterone is a topic of significant interest in the realm of endocrinology and men’s health. Research has suggested that there is a positive correlation between vitamin D levels and testosterone levels in men. Studies have indicated that men with higher levels of vitamin D tend to have higher levels of testosterone, and conversely, men with vitamin D deficiency are more likely to have lower testosterone levels.
The Role of Vitamin D in Testosterone Production
Vitamin D is believed to play a crucial role in the regulation of testosterone production. It is thought to influence the expression of genes involved in testosterone synthesis. The mechanisms underlying this relationship are complex and multifaceted, involving various biochemical pathways. Some key aspects of this relationship include:
- The presence of vitamin D receptors in the testes, which suggests a direct role of vitamin D in testicular function.
- The influence of vitamin D on the steroidogenic pathway, which is critical for the production of testosterone.
- The potential for vitamin D deficiency to disrupt the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to decreased testosterone production.
Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on Testosterone Levels
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to low testosterone levels in numerous studies. The deficiency can lead to a decrease in the production of testosterone, potentially resulting in hypogonadism. The effects of vitamin D deficiency on testosterone levels can be significant and may manifest as:
- Reduced libido and erectile dysfunction due to the decreased levels of testosterone.
- Decreased muscle mass and strength, as testosterone plays a key role in muscle physiology.
- Increased body fat, particularly around the abdominal area, which can further exacerbate hormonal imbalances.
Vitamin D Supplementation and Testosterone
The supplementation of vitamin D has been explored as a potential strategy to enhance testosterone levels, particularly in individuals with vitamin D deficiency. While the evidence is not yet conclusive, some studies suggest that vitamin D supplementation can lead to an increase in testosterone levels. Key considerations include:
- The need for adequate dosing of vitamin D to achieve sufficient levels.
- The importance of monitoring vitamin D levels to avoid toxicity.
- The potential for individual variability in response to vitamin D supplementation, highlighting the need for personalized approaches.
How much vitamin D per day for a man to increase testosterone?
![]()
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D for men to increase testosterone levels is a topic of ongoing research. Studies suggest that maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is essential for optimal testosterone production. The optimal dosage may vary depending on factors such as age, geographical location, and individual health status.
The Importance of Vitamin D for Testosterone Production
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy testosterone levels in men. Research has shown that vitamin D receptors are present in the testes, and vitamin D deficiency has been linked to low testosterone levels. Ensuring adequate vitamin D intake is essential for supporting testosterone production.
- Vitamin D Receptors are present in the testes, indicating a direct role in testosterone production.
- Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to low testosterone levels in several studies.
- Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels may help support optimal testosterone production.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin D for Men
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies depending on factors such as age and health status. The Endocrine Society recommends that adults take 1,500-2,000 IU of vitamin D per day. However, some studies suggest that higher doses may be necessary to achieve optimal testosterone levels.
- The Endocrine Society recommends 1,500-2,000 IU of vitamin D per day for adults.
- Some studies suggest that higher doses (4,000-5,000 IU/day) may be necessary for optimal testosterone levels.
- Individual factors such as age and health status may influence the optimal dosage.
Factors Influencing Vitamin D Levels and Testosterone Production
Several factors can influence vitamin D levels and testosterone production in men. These include age, geographical location, skin pigmentation, and lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise. Understanding these factors is essential for maintaining optimal vitamin D levels and supporting testosterone production.
- Age is a significant factor, as older men are more likely to experience vitamin D deficiency.
- Geographical location and skin pigmentation can influence vitamin D production in the skin.
- Lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise can also impact vitamin D levels and testosterone production.
What does too much vitamin D do to a man?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/symptoms-of-too-much-vitamin-d-5105134_final1-eb2f19a74bd54a80950644df25ccb5b2.png)
Too much vitamin D can cause a range of health problems in men. Hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by elevated calcium levels in the blood, is one of the primary concerns. This occurs because vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels in the body. When there’s too much vitamin D, it can lead to an excessive absorption of calcium from the diet, causing a buildup of calcium in the blood.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Toxicity
Vitamin D toxicity can manifest through various symptoms, including nausea and vomiting, weakness, and abnormal heart rhythms. These symptoms arise due to the elevated calcium levels in the blood, which can affect multiple bodily systems. The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the extent of the toxicity.
- Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and constipation are common due to the effect of high calcium levels on the digestive system.
- Musculoskeletal symptoms like weakness and muscle pain can occur as a result of the impact of hypercalcemia on muscle function.
- Cardiovascular effects, including abnormal heart rhythms, can be potentially serious complications of vitamin D toxicity.
Long-term Effects of Excessive Vitamin D
Prolonged excessive intake of vitamin D can lead to more serious health issues, including kidney damage and calcification of joints and soft tissues. The kidneys are particularly vulnerable as they try to filter out the excess calcium, which can lead to kidney stones and impaired kidney function over time.
- Kidney stones are a significant risk due to the high concentration of calcium in the urine, which can crystallize and form stones.
- Calcification of soft tissues, including joints and arteries, can occur as calcium deposits form in these areas, potentially leading to pain and dysfunction.
- Osteoporosis might seem counterintuitive as a risk of vitamin D excess, given vitamin D’s role in bone health, but excessive levels can lead to an imbalance in bone remodeling.
Prevention and Management
Preventing vitamin D toxicity involves being mindful of vitamin D intake, especially for individuals taking supplements. It’s essential to have regular blood tests to monitor vitamin D and calcium levels, particularly for those at risk or on high-dose supplements.
- Monitoring vitamin D levels is crucial for individuals on supplements to avoid reaching toxic levels.
- Adjusting supplement dosages based on regular blood tests can help prevent toxicity.
- Being aware of dietary sources of vitamin D, such as fortified foods and fatty fish, can also help manage overall vitamin D intake.
What vitamin blocks testosterone levels?

Vitamin B, specifically Vitamin B6 and Vitamin B12, when taken in high doses, can potentially block or lower testosterone levels. However, the most relevant vitamin associated with this effect is Vitamin D when its levels are excessively high or imbalanced, but generally, it’s more about maintaining optimal levels rather than blocking testosterone directly.
The Role of Vitamins in Testosterone Production
Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance, including testosterone levels. While some vitamins are essential for testosterone production, an excessive intake of certain vitamins can have a negative impact. For instance, Vitamin D is known to be associated with testosterone levels, and maintaining optimal levels is crucial.
- Vitamin D Receptors are present in areas of the brain that are involved in the regulation of testosterone.
- Deficiencies in Vitamin D have been linked to lower testosterone levels.
- However, excessively high levels of Vitamin D can lead to imbalances.
Vitamins and Testosterone: The Balance
The relationship between vitamins and testosterone is complex and involves a delicate balance. While vitamins are essential nutrients, excessive intake, especially through supplementation, can lead to imbalances that may affect testosterone levels. It’s crucial to understand that both deficiencies and excessive levels of certain vitamins can have negative effects.
- A balanced diet that includes essential vitamins is necessary for maintaining healthy testosterone levels.
- Supplementation should be approached with caution and ideally under professional guidance.
- Regular monitoring of vitamin levels and hormonal balance is recommended for individuals considering long-term supplementation.
Potential Effects of Excessive Vitamin Intake on Testosterone
Excessive intake of certain vitamins can have unforeseen effects on hormonal balance, including testosterone levels. Understanding the potential risks associated with high doses of vitamins is essential for maintaining overall health and hormonal balance.
- High doses of Vitamin C and Vitamin E may interact with other bodily processes that could indirectly affect testosterone.
- The impact of vitamins on testosterone can vary significantly between individuals due to factors like genetic differences and overall health.
- Maintaining a balanced intake of vitamins through a varied diet is generally recommended over relying heavily on supplementation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between Vitamin D and Testosterone levels?
The connection between Vitamin D and Testosterone levels is a topic of significant interest in the realm of men’s health. Research has indicated that there is a positive correlation between Vitamin D levels and Testosterone production. Studies have shown that individuals with Vitamin D deficiency tend to have lower levels of Testosterone, while those with adequate Vitamin D levels tend to have higher Testosterone levels. This suggests that maintaining optimal Vitamin D levels may be essential for supporting healthy Testosterone production.
How does Vitamin D impact Testosterone production?
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy Testosterone production by influencing the expression of genes involved in Testosterone synthesis. It is believed that Vitamin D helps to regulate the function of Leydig cells, which are responsible for producing Testosterone in the testes. Additionally, Vitamin D may also help to mitigate the negative effects of inflammation and oxidative stress on Testosterone production, thereby supporting overall reproductive health.
Can Vitamin D supplements boost Testosterone levels?
While some studies suggest that Vitamin D supplementation may help to increase Testosterone levels, particularly in individuals with Vitamin D deficiency, the evidence is not yet conclusive. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before initiating any supplementation regimen, as individual results may vary. Furthermore, it is also important to address other factors that may be influencing Testosterone levels, such as diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle.
What are the benefits of maintaining optimal Vitamin D and Testosterone levels?
Maintaining optimal levels of both Vitamin D and Testosterone is crucial for overall health and well-being. Testosterone plays a vital role in maintaining muscle mass, bone density, and libido, while Vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health and supporting immune function. By maintaining optimal levels of both Vitamin D and Testosterone, individuals can potentially reduce their risk of developing conditions such as osteoporosis, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.