Vitamin D and testosterone are two essential components that play crucial roles in maintaining overall health and well-being in individuals. Research has uncovered a significant correlation between the levels of vitamin D and testosterone in the body. Studies indicate that a deficiency in vitamin D can lead to lower testosterone levels, which may result in various health issues, including decreased libido, fatigue, and osteoporosis. Understanding the link between vitamin D and testosterone can provide valuable insights into maintaining optimal levels of these vital nutrients and promoting better overall health.

The Connection Between Vitamin D and Testosterone Levels
The relationship between Vitamin D and Testosterone has been a subject of interest in the medical community due to its implications on overall health and wellbeing. Research has indicated that there is a significant link between the levels of Vitamin D and Testosterone in the body. Testosterone, a crucial hormone in the human body, is responsible for a variety of functions including muscle mass, bone density, and sex drive. Similarly, Vitamin D, often referred to as the sunshine vitamin, plays a vital role in bone health and has been associated with various other health benefits.
The Role of Vitamin D in Testosterone Production
Studies have suggested that Vitamin D may play a role in the production and regulation of Testosterone. The mechanism behind this is not entirely understood, but it’s believed that Vitamin D receptors in the testes, where Testosterone is produced, could influence Testosterone synthesis. Men with Vitamin D deficiency have been found to have lower levels of Testosterone, indicating a potential link between the two. | Vitamin D Level | Testosterone Level | Health Implication | | — | — | — | | Deficient | Low | Increased risk of osteoporosis and decreased libido | | Insufficient | Borderline | Potential impact on muscle mass and bone density | | Sufficient | Normal | Optimal health and wellbeing |
Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency on Testosterone Levels
A deficiency in Vitamin D has been correlated with lower levels of Testosterone. This is particularly concerning as both conditions can have significant health implications. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to weakened bones, while low Testosterone can result in decreased muscle mass, reduced sex drive, and other symptoms. | Condition | Effect on Testosterone | Effect on Vitamin D | | — | — | — | | Vitamin D Deficiency | Decrease | – | | Low Testosterone | – | Potential decrease due to related lifestyle factors | | Obesity | Can lead to lower Testosterone | Often associated with lower Vitamin D levels |
Seasonal Variations in Vitamin D and Testosterone
Interestingly, both Vitamin D and Testosterone levels have been observed to vary with the seasons. During the winter months, when sunlight is scarce, Vitamin D levels tend to drop, and similarly, Testosterone levels have been found to be lower. This seasonal variation underscores the potential link between Vitamin D and Testosterone. | Season | Vitamin D Level | Testosterone Level | | — | — | — | | Winter | Lower | Lower | | Summer | Higher | Higher |
Maintaining Healthy Levels of Vitamin D and Testosterone
To maintain healthy levels of both Vitamin D and Testosterone, a combination of lifestyle changes and, if necessary, supplements can be beneficial. Regular exposure to sunlight, a balanced diet, and exercise are crucial. For individuals with deficiencies, Vitamin D supplements can help improve Testosterone levels. | Method | Effect on Vitamin D | Effect on Testosterone | | — | — | — | | Sunlight Exposure | Increase | Potential indirect increase | | Vitamin D Supplements | Increase | Potential increase | | Exercise | No direct effect | Can help increase |
Future Research Directions on Vitamin D and Testosterone
While the current evidence suggests a link between Vitamin D and Testosterone, further research is needed to fully understand the nature of this relationship. Studies examining the effects of Vitamin D supplementation on Testosterone levels could provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic applications. | Research Area | Potential Outcome | Implication | | — | — | — | | Vitamin D and Testosterone correlation | Clarify the relationship | Better understanding of health implications | | Effects of Vitamin D supplementation | Potential increase in Testosterone | Therapeutic applications for low Testosterone |
How much vitamin D per day for a man to increase testosterone?
![]()
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D for men to support testosterone production is a topic of ongoing research. Studies have shown that vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy testosterone levels. The optimal dosage is still being debated, but most research suggests that a daily intake of 1,000-2,000 IU (International Units) of vitamin D is sufficient to support testosterone production.
Vitamin D and Testosterone: The Science
Research has shown that vitamin D receptors are present in the testes, and vitamin D deficiency has been linked to low testosterone levels. Studies have also demonstrated that vitamin D supplementation can increase testosterone production in men with vitamin D deficiency. The mechanisms behind this are not fully understood, but it’s thought that vitamin D helps to regulate the expression of genes involved in testosterone production. Key factors to consider include:
- The role of vitamin D receptors in the testes and their impact on testosterone production
- The relationship between vitamin D deficiency and low testosterone levels
- The potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation in men with vitamin D deficiency
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin D
The optimal daily intake of vitamin D for men is still a topic of debate. The Institute of Medicine recommends a daily intake of 600-800 IU of vitamin D for adults, but some research suggests that higher doses may be necessary to support testosterone production. Factors to consider when determining the optimal daily intake include:
- Skin pigmentation, as darker skin types may require higher doses of vitamin D
- Age, as older men may require higher doses due to decreased vitamin D production
- Body composition, as obese men may require higher doses due to increased vitamin D sequestration
Potential Risks and Benefits of Vitamin D Supplementation
While vitamin D supplementation may be beneficial for men with vitamin D deficiency, there are also potential risks to consider. High doses of vitamin D can cause hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by elevated calcium levels in the blood. Other potential risks include:
- Kidney stone formation due to increased calcium excretion
- Interactions with medications, such as calcium channel blockers
- Over-suppression of parathyroid hormone, leading to an increased risk of adynamic bone disease
Which vitamins increase testosterone levels?

Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, including the production of hormones such as testosterone. Certain vitamins have been identified as having a positive impact on testosterone levels.
Key Vitamins for Testosterone Production
The production of testosterone is influenced by several vitamins, with Vitamin D, Vitamin B, and other nutrients being particularly significant. Research has shown that maintaining adequate levels of these vitamins is essential for supporting testosterone production.
Some of the key vitamins that contribute to healthy testosterone levels include:
- Vitamin D: often considered a hormone itself, Vitamin D has been linked to testosterone production, with deficiencies in Vitamin D associated with lower testosterone levels.
- Vitamin B: The B vitamins, especially B6, B9 (Folate), and B12, play roles in the synthesis of testosterone and the maintenance of healthy reproductive cells.
- Vitamin K: Though less directly linked to testosterone than Vitamin D or B vitamins, Vitamin K is important for overall health and may indirectly support hormone production.
The Role of Antioxidant Vitamins
Antioxidant vitamins are also crucial for maintaining healthy testosterone levels by reducing oxidative stress, which can negatively impact testosterone production. Vitamins C and E are notable antioxidants that help protect the testes from oxidative damage, thereby supporting testosterone production.
Some key antioxidant vitamins and their roles include:
- Vitamin C: helps in reducing oxidative stress and is involved in the production of testosterone.
- Vitamin E: acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage and supporting overall reproductive health.
- Other Antioxidants: While not vitamins, other antioxidants like Selenium and Zinc also play critical roles in protecting the testes and supporting testosterone production.
Maintaining Optimal Vitamin Levels for Testosterone
To maximize the potential benefits of vitamins on testosterone levels, it’s essential to maintain optimal vitamin levels through a balanced diet and, if necessary, supplementation. Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals that support testosterone production can be achieved through a combination of dietary adjustments and targeted supplements.
Key strategies for maintaining optimal vitamin levels include:
- Dietary Balance: consuming a diet rich in foods that are natural sources of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Supplementation: using supplements to fill any nutritional gaps, especially for vitamins known to impact testosterone levels.
- Regular Health Checks: monitoring vitamin levels and overall health to identify any deficiencies or areas for improvement.
How does vitamin D interact with hormones?
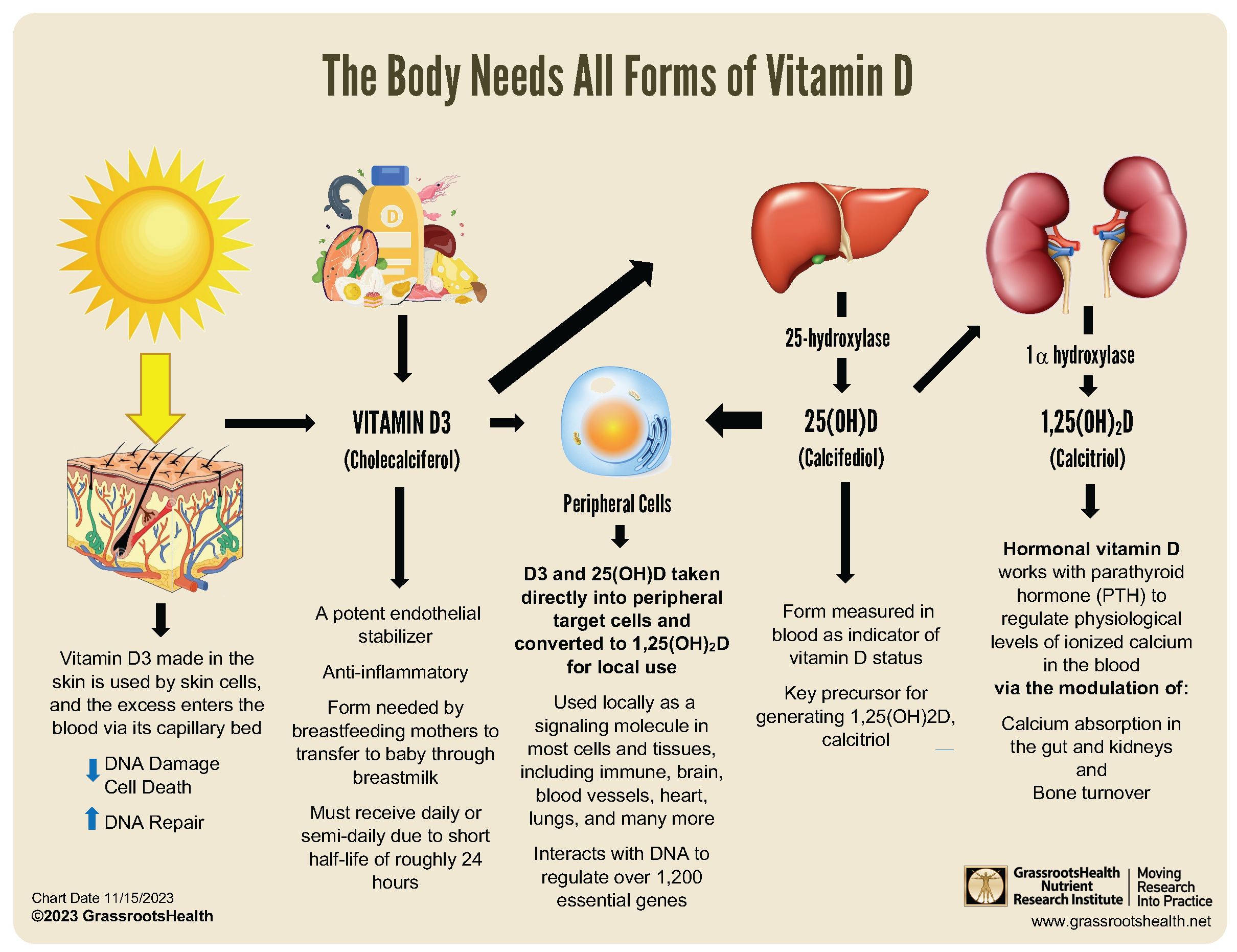
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, immune function, and cell growth. It interacts with various hormones in the body to regulate different physiological processes. One of the primary ways vitamin D interacts with hormones is by modulating the expression of genes involved in hormone regulation. Vitamin D receptors (VDRs) are present in various tissues, including the parathyroid gland, pancreas, and thyroid gland, where they influence the production and secretion of hormones.
Regulation of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Vitamin D helps regulate the production of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is essential for maintaining calcium homeostasis. When vitamin D levels are adequate, it suppresses the production of PTH, thereby preventing an overproduction of PTH, which can lead to bone resorption. The regulation of PTH by vitamin D involves:
- Inhibition of PTH gene expression: Vitamin D binds to VDRs in the parathyroid gland, inhibiting the transcription of the PTH gene.
- Regulation of calcium levels: Vitamin D helps maintain optimal calcium levels, which in turn regulates PTH secretion.
- Modulation of parathyroid gland function: Vitamin D influences the growth and function of parathyroid gland cells.
Interaction with Thyroid Hormones
Vitamin D also interacts with thyroid hormones, which play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may be associated with an increased risk of thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The interaction between vitamin D and thyroid hormones involves:
- Regulation of thyroid gland function: Vitamin D may influence the production and secretion of thyroid hormones.
- Modulation of immune responses: Vitamin D helps regulate immune responses, which can affect thyroid gland function.
- Maintenance of thyroid hormone homeostasis: Vitamin D may help maintain optimal levels of thyroid hormones in the body.
Influence on Insulin and Glucose Metabolism
Vitamin D has been shown to influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, which are critical for maintaining energy homeostasis. The interaction between vitamin D and insulin involves:
- Regulation of insulin secretion: Vitamin D may influence the production and secretion of insulin from the pancreas.
- Modulation of insulin sensitivity: Vitamin D helps regulate insulin sensitivity, which affects glucose uptake in cells.
- Influence on glucose metabolism: Vitamin D may influence glucose metabolism, which can impact the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What does too much vitamin D do to a man?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/symptoms-of-too-much-vitamin-d-5105134_final1-eb2f19a74bd54a80950644df25ccb5b2.png)
Too much vitamin D can cause a range of health problems in men. When vitamin D levels become excessively high, it can lead to a condition known as hypervitaminosis D. This occurs when the body has too much calcium in the blood, which can cause a variety of symptoms.
Symptoms of Excessive Vitamin D
Excessive levels of vitamin D can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea and vomiting, weakness, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can also lead to more serious health problems, such as kidney damage and heart problems.
- Nausea and vomiting: High levels of vitamin D can cause stomach upset, leading to nausea and vomiting.
- Weakness and fatigue: Excessive vitamin D can cause muscle weakness and fatigue, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Kidney damage: Prolonged high levels of vitamin D can cause damage to the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease.
Effects on Calcium Levels
One of the primary concerns with excessive vitamin D is its impact on calcium levels in the blood. Vitamin D helps regulate calcium levels, but too much vitamin D can cause hypercalcemia, a condition characterized by elevated calcium levels.
- Hypercalcemia: High levels of calcium in the blood can cause a range of symptoms, including confusion, weakness, and kidney stones.
- Calcium deposits: Excessive calcium can deposit in various tissues, including the kidneys, liver, and heart.
- Bone health: While vitamin D is essential for bone health, excessive levels can cause bone pain and other skeletal problems.
Long-term Consequences
Prolonged excessive intake of vitamin D can have long-term consequences, including kidney damage and cardiovascular disease. It is essential to monitor vitamin D levels and maintain a balanced intake to avoid these complications.
- Kidney damage: Prolonged hypercalcemia can cause irreversible damage to the kidneys.
- Cardiovascular disease: Excessive vitamin D can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Mineral imbalance: High levels of vitamin D can disrupt the balance of other essential minerals, including magnesium and potassium.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between Vitamin D and Testosterone levels?
The connection between Vitamin D and Testosterone has been a subject of interest in recent years. Research has shown that there is a positive correlation between the levels of Vitamin D and Testosterone in men. Studies have indicated that individuals with Vitamin D deficiency tend to have lower levels of Testosterone, which can lead to various health issues such as decreased libido, fatigue, and decreased muscle mass. On the other hand, maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin D through sun exposure, diet, or supplementation may support healthy Testosterone production.
How does Vitamin D affect Testosterone production?
Vitamin D plays a significant role in maintaining healthy Testosterone levels by influencing the expression of genes involved in Testosterone synthesis. The presence of Vitamin D receptors in the Leydig cells of the testes, which are responsible for producing Testosterone, suggests a direct link between Vitamin D and Testosterone production. Moreover, Vitamin D helps regulate the expression of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of Testosterone, thereby supporting the production of this crucial hormone.
Can Vitamin D supplementation increase Testosterone levels?
Several studies have investigated the potential of Vitamin D supplementation to boost Testosterone levels. While the evidence is not yet conclusive, some research suggests that Vitamin D supplementation can help increase Testosterone levels in individuals with Vitamin D deficiency. However, it is essential to note that the effectiveness of Vitamin D supplementation in raising Testosterone levels may vary depending on individual factors such as age, health status, and the presence of underlying medical conditions.
What are the benefits of maintaining healthy Vitamin D and Testosterone levels?
Maintaining healthy levels of both Vitamin D and Testosterone is crucial for overall well-being. Adequate Testosterone levels support muscle mass, bone density, and libido, while Vitamin D is essential for bone health and immune function. Furthermore, healthy levels of both Vitamin D and Testosterone have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as osteoporosis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Ensuring adequate levels of these essential nutrients through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and supplementation (if necessary) can have a significant impact on overall health and quality of life.